Commodities and Units
Commodities and Units lists all system and custom commodity types.
Settings should only be modified by an administrator who understands the outcome of making unit changes. This powerful feature makes system-wide changes.
Typically these settings are configured during the initial setup, however, new reporting requirements may require you to make changes.
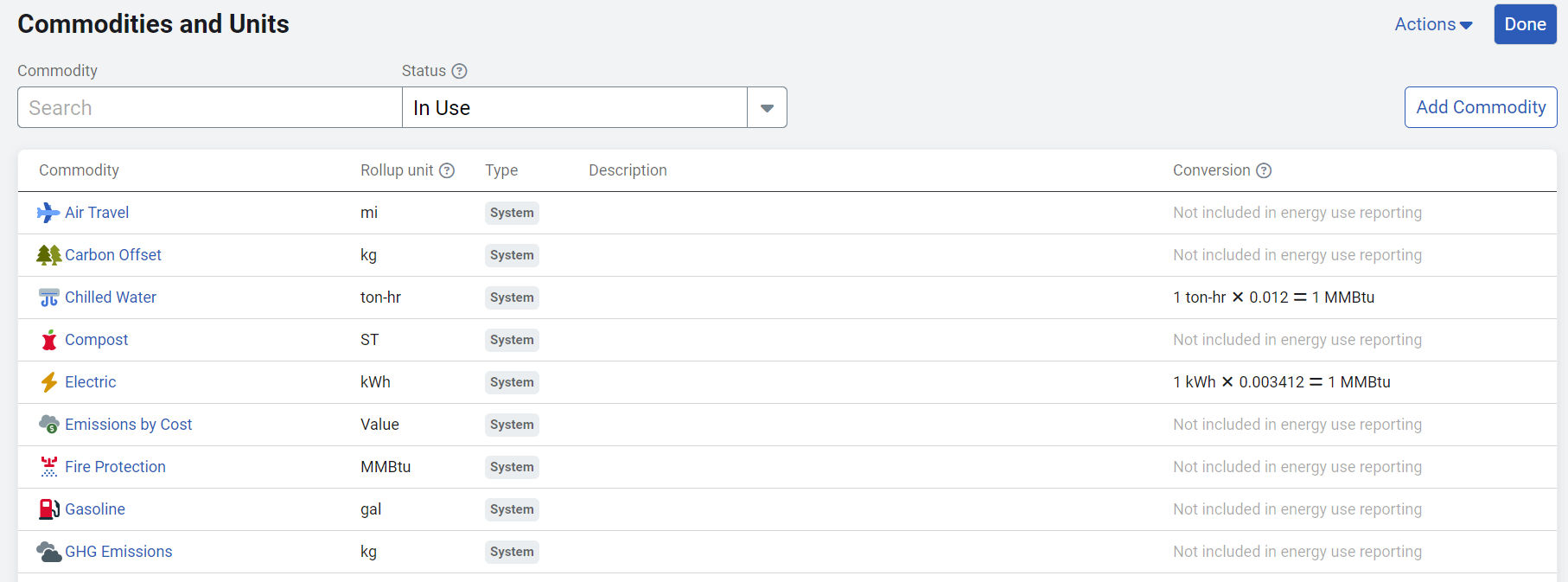
Add Commodity
Steps to add a custom commodity.
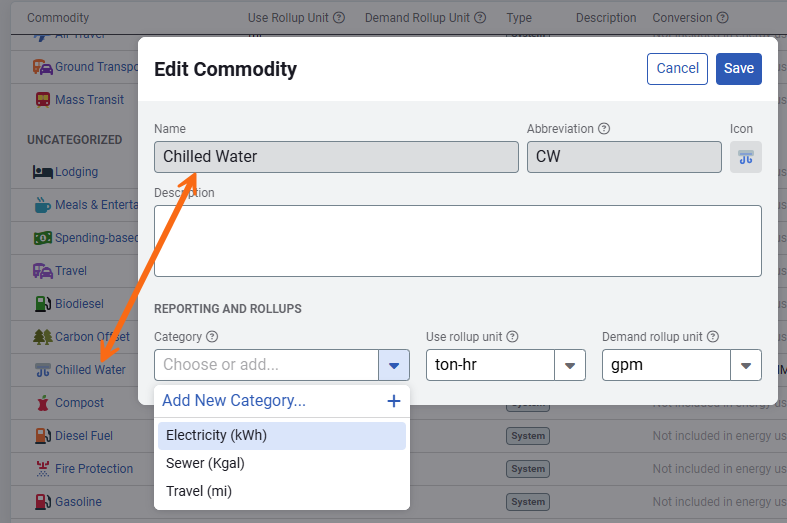
- Click Add Commodity.
- Enter the name.
- Enter the abbreviation. This is a unique 3 letter abbreviation for this commodity. This abbreviation is automatically added to the meter name during the creation process. For custom commodities this is also the commodity code.
*For system commodities, the abbreviation is not the commodity code. To see the commodity code for system commodities hover over the name in the table to see the code in brackets.
Use rollup unit
The rollup unit is the common use unit for reporting purposes. You can select an existing unit or create a new one with setup spreadsheets.
- Default unit of measure for each commodity.
- It's required because because vendors may use different reporting units on bills.
- For example, vendors may use different units for reporting natural gas use such as MCF and THERM. The Rollup unit converts the various natural gas units into one unit for reports and benchmarks.
Demand rollup unit
When you select a demand rollup unit the commodity also reports on demand.
Meters must have bills with demand data to report on demand.
Conversion information
When you select a rollup unit other than energy, you can select if the commodity should be converted to energy and then enter the conversion information.
Rollup unit categories
- Cost only (no rollup unit)
- Volume
- Weight
- Energy
- Counter
- Time
- Area
- Other
- Rate of Mass
- Temperature
- Velocity
- Pressure
- Concentration
- Frequency
- Rate of Volume
- Rate of Energy
- Current
- Voltage
- GHG
Add a category
You can group commodities into categories. This is useful to track commodities because it gives you more granularity when reporting on overall use and cost.
Four default categories are automatically created for you. These commodity categories can be changed or deleted depending on your reporting needs.
When you create a category you set the rollup unit, any commodity you add inherits this rollup unit.
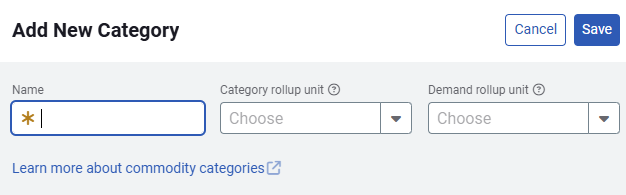
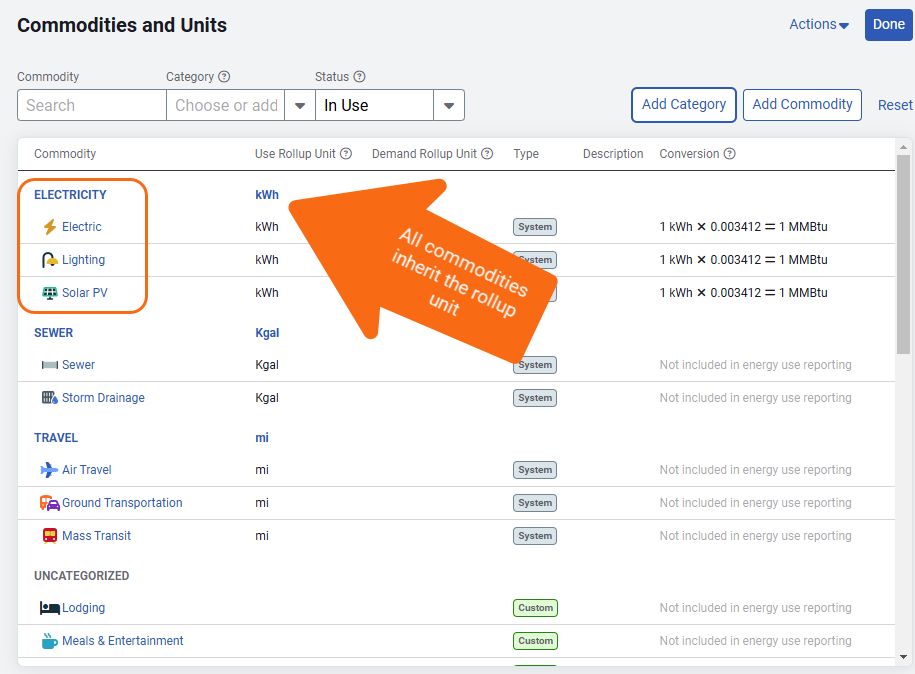
Add a commodity to a category
To add a commodity to a a category, click the commodity name to open the edit dialog. You can select an existing category or create a new one.
Data Reporting Settings
Data Reporting Settings lets you configure the units to use in charts and maps.
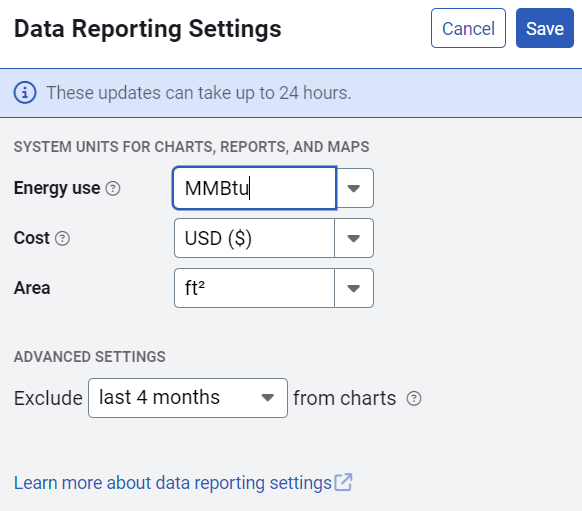
Energy use
Energy use units let you add together unlike energy resources for reporting. The meter use unit is always used for meter reporting.
Cost
This sets your system currency, this is used by default in bills and records. You can override this setting when viewing bills and records if needed.
Area
Decide how you want floor area displayed.
Advanced Settings
This option lets you exclude data from the last full specified months from charts in dashboards. For example, if the current month is September and last 2 months is selected, September, August, and July would be excluded from charts.
This setting does not apply to dashboard charts set to a specific date range or any reports.
Units to use in charts and maps
- Unit of measure used for any chart or report at any level of the organization that requires units of unlike energy commodities to be added together.
- Used in Groups and Benchmarks module, Energy Use Intensity, and other reports.
- Commodities that cannot be converted to energy, such as water or refuse, are not included.
- Three options MMBtu, Kbtu, and ekWh
- KBtu (thousands of BTU) is the recommended global unit of measure because it is the one most frequently used in building benchmarks and all ENERGY STAR reporting.
- The units of annual KBtu per square foot are easy to manage and read; they typically fall in a broad range of 25 to 250 KBtu per Square foot.
- MMBtu (millions of BTU) is 1,000 times larger than a kBTU, so values of MMBtu and MMBtu per square foot are 1,000 times less. A building may have a EUI value of 0.050 MMBtu per square foot, which may be less friendly to read.
- MMBtu is normally preferred by manufacturers and other bulk energy consumers because they are more focused on total energy use and use per unit of production.
Units of measure defined
| EnergyCAP | ENERGY STAR | |
| C | 100 | 100 |
| K | 1,000 | 1,000 |
| M | 1,000 | 1,000,000 |
EnergyCAP defines BOTH K and M as 1,000.
MBtu (thousand) and MMBtu (million) are not equivalent.
When you submit utility bills to ENERGY STAR, UtilityManagement maps your commodity use to the appropriate ENERGY STAR unit. Check the ENERGY STAR Supported Commodities page to note the meter unit in the PM column. Verify the units for the Portfolio Manager meter match what is listed in this column.
Example
For the commodity steam, Klb and Mlb are the same in EnergyCAP, both convert to 1,000 pounds.
On the ENERGY STAR Supported Commodities, you see the Meter Unit in PM listed as Klbs (thousand pounds). In Portfolio Manager, make sure steam meters are set up with Klbs (thousand pounds) as their unit of measure.
Steam bills in EnergyCAP can be entered in any of EnergyCAP's steam units, when submitting to ENERGY STAR the units get converted to Klbs.
Use units in reporting
- Bills and records are shown in their native unit.
- Meters and emissions sources or single commodities display in the rollup unit.
- Buildings and organizations with multiple commodities use the reporting unit.