Commodities and Units
The Commodities and Units screen lists all system-defined and custom commodity types (like electricity, water, and natural gas) and their units of measure.
Only administrators should make changes to these settings. Updating commodities or units affects the entire system and may impact billing, reporting, and data accuracy.
These settings are typically configured during initial setup but can be updated to support new reporting or business requirements.
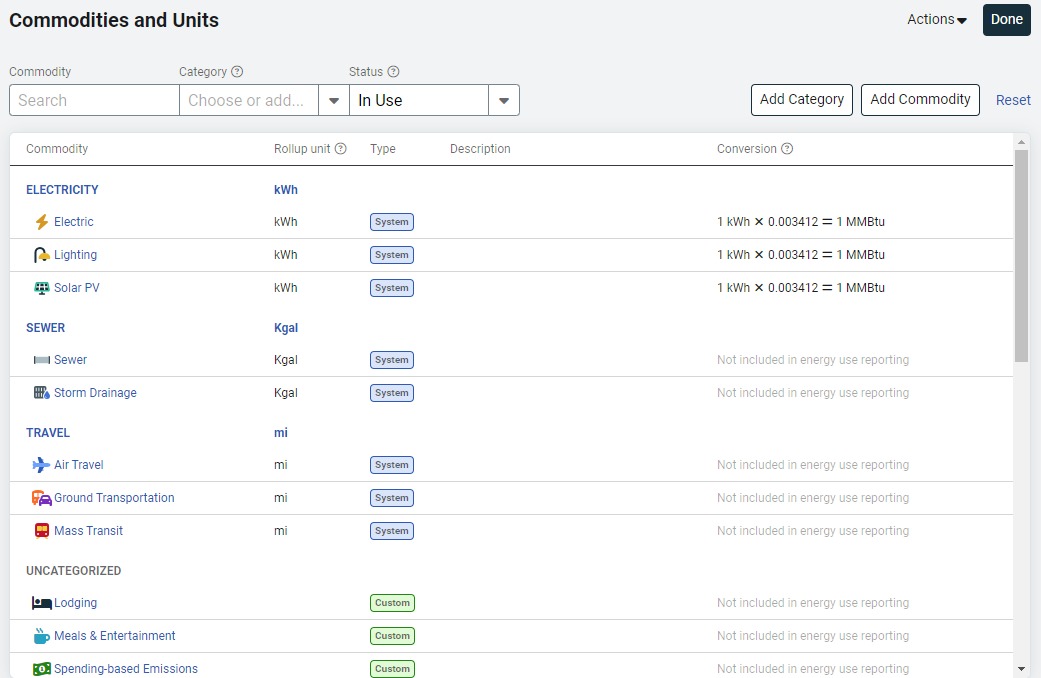
Steps to add a commodity
- Go to Settings (Gear icon).
- In Commodities and Units, click Add Commodity.
- Enter the commodity name.
- Enter a 3-letter abbreviation:
- This serves as the commodity code.
- It must be unique.
- The code is automatically added to the meter name when a new meter is created. For example, Building01 - ELE01.
Note: For system commodities, the abbreviation is not the commodity code. To see the commodity code for system commodities hover over the commodity name in the Commodities and Units table to view the code in brackets.
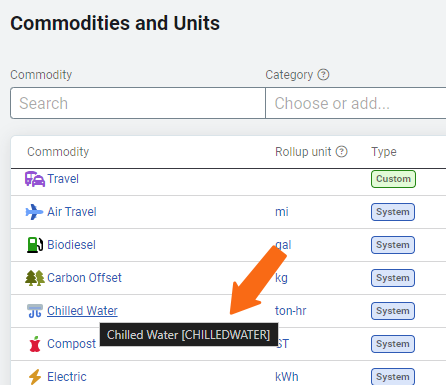
Use rollup unit
The rollup unit is the common use unit for consistent reporting. It converts all use values to a common unit—which is helpful when vendors report use in different units.
- Each commodity has a default rollup unit.
- You can select an existing unit or create a new one using setup spreadsheets.
- A rollup unit is required when vendor data includes multiple units.
For example, vendors may report natural gas in different units, such as MCF and THERM. The rollup unit converts these into one consistent unit for use in reports and benchmarks.
Demand rollup unit
When you select a demand rollup unit, the commodity also includes demand values in reports.
Note: Meters must have bills that include demand data for demand reporting to work.
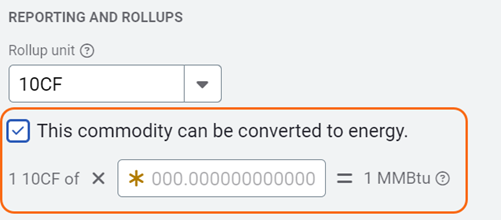
Conversion information
When you select a rollup unit that is not an energy unit, you can choose to convert the commodity to an energy equivalent.
- Check the Convert to Energy option.
- Enter the conversion factor to define how the commodity is translated into energy use.
Rollup unit categories
- Cost only (no rollup unit)
- Volume
- Weight
- Energy
- Counter
- Time
- Area
- Other
- Rate of Mass
- Temperature
- Velocity
- Pressure
- Concentration
- Frequency
- Rate of Volume
- Rate of Energy
- Current
- Voltage
- Emissions
Add a category
You can group commodities into categories to improve reporting on use and cost. Categories help you organize data for more detailed and flexible reports.
- EnergyCAP provides four default categories. You can edit or delete these to match your reporting needs.
- When you create a new category, you must assign a rollup unit (such as kWh or gallons). All commodities added to the category use this rollup unit for summaries.
✅ Use categories to simplify tracking, comparing, and reporting across similar commodities.

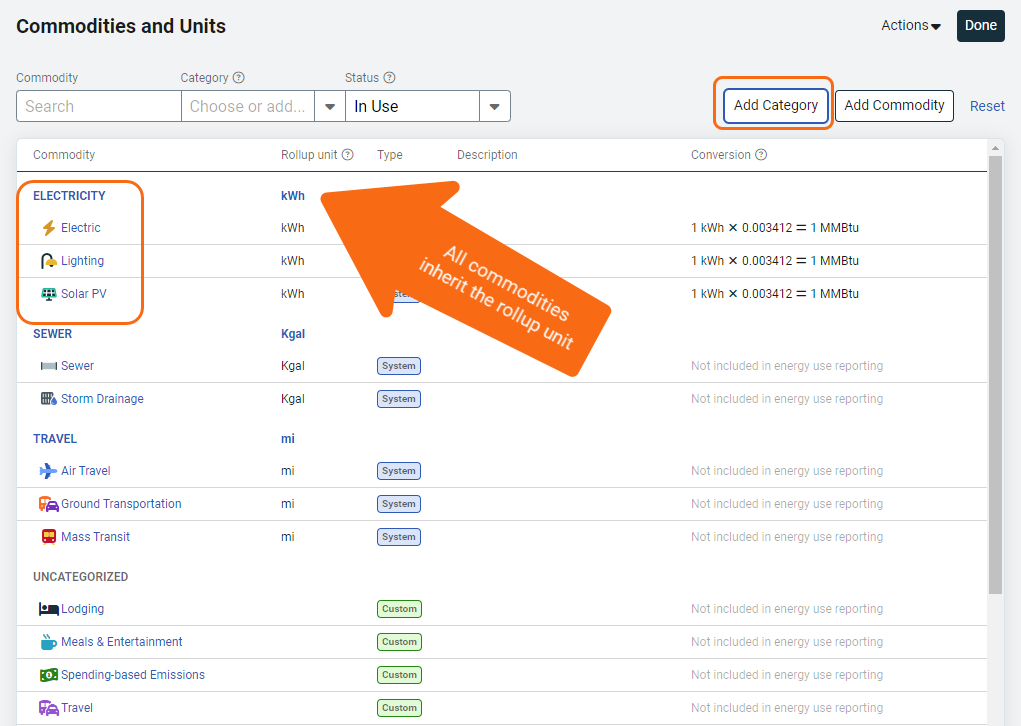
Add a commodity to a category
To add a commodity to a category, click the commodity name to open the edit dialog. You can select an existing category or create a new one.
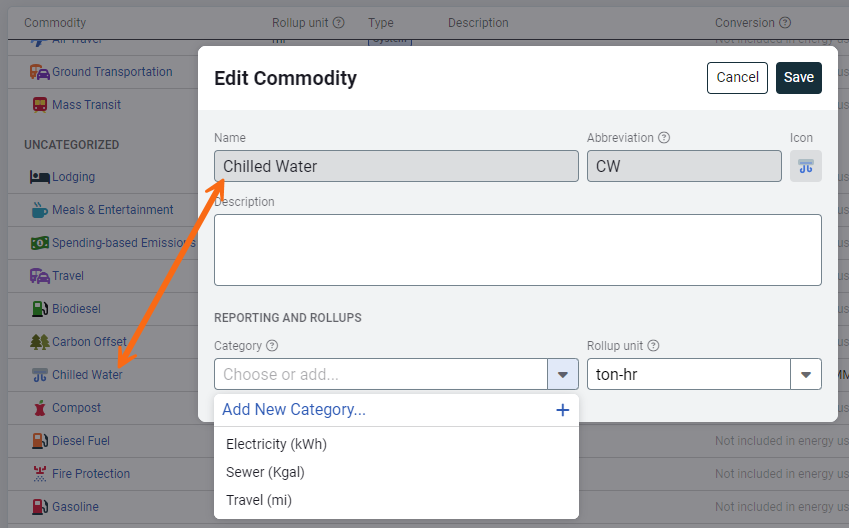
Remove a commodity from a category
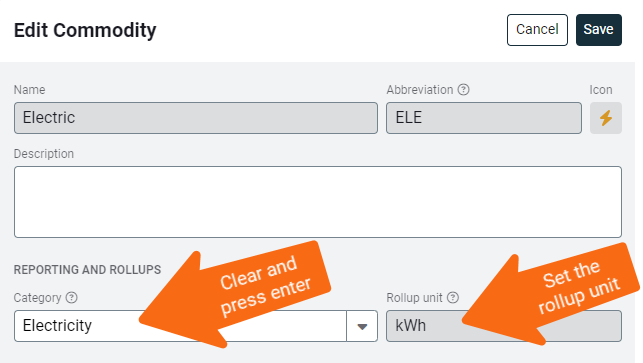
- Click the commodity link.
- Clear the Category selection for the commodity and press the Enter key.
- Set the Use rollup unit for the commodity.
- Press Save to remove the commodity from the category.
Data Reporting Settings
Use Data Reporting Settings to choose how data is displayed throughout the application. These settings affect units, currency, and visualizations across dashboards and reports.
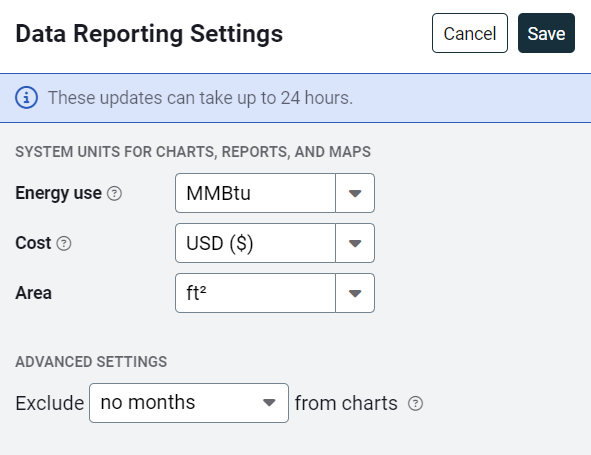
Energy use
- Choose a standard energy unit (like Kbtu or MWh) to combine different energy types (electricity, gas, etc.) in reports.
- Note: The meter's original unit is always used when viewing meter-level data.
Cost
- Set your default system currency (for example, USD, CAD).
- This currency appears on bills and records by default. You can override it as needed when viewing specific bills.
Area
- Select how floor area should be displayed (for example, square feet or square meters).
Exclude months from charts
- You can exclude recent months from dashboard charts to avoid showing incomplete data.
- Example: If the current month is September and you select Last 2 Months, the system excludes September, August, and July.
This setting only applies to dashboard charts using dynamic date ranges. It does not apply to charts with fixed date ranges or to any reports.
More about energy use units
This setting defines the unit of measure used in charts and reports when unlike energy commodities (for example, electricity and natural gas) are combined. It applies across various modules like:
- Groups and Benchmarks
- Energy Use Intensity (EUI)
- Other energy-related reports
🚫 Commodities that can't be converted to energy (like water or refuse) are not included.
Available units
You can choose from a variety of different energy units. For example:
| Unit | Description | Best for |
| kBtu (thousands of BTU) | Commonly used in ENERGY STAR and building benchmarks | Buildings, benchmarking, ENERGY STAR reporting. |
| MMBtu (millions of BTU) | 1,000 times larger than kBtu. Used for measuring large-scale energy use. | Manufacturing, industrial reporting. |
| ekWh (equivalent kilowatt-hour) | Converts all energy types to equivalent kWh. | Use if your organization prefers electricity-equivalent units. |
Units of measure defined
| EnergyCAP | ENERGY STAR | |
| C | 100 | 100 |
| K | 1,000 | 1,000 |
| M | 1,000 | 1,000,000 |
- EnergyCAP defines BOTH K and M as 1,000.
- MBtu (thousand) and MMBtu (million) are not equivalent.
When you submit utility bills to ENERGY STAR, EnergyCAP maps your commodity use to the appropriate ENERGY STAR unit. Check the ENERGY STAR Supported Commodities section to note the meter unit in the PM column. Verify the units for the Portfolio Manager meter match what is listed in this column.
Example: Steam units
In EnergyCAP the units Klb and Mlb are treated the same—both represent 1,000 pounds of steam.
ENERGY STAR note:
On the ENERGY STAR Supported Commodities page, Portfolio Manager (PM) lists the steam meter unit as Klbs (thousand pounds). When setting up steam meters in PM, make sure to use Klbs as the unit of measure.
Submitting steam data
- In EnergyCAP, you can enter steam bills using as of the available steam units.
- When you submit data to ENERGY STAR, EnergyCAP automatically converts the unit to Klbs.
Use units in reporting
Different parts of the system use different units based on the type of data and level of detail:
- Bills and records
Display using the original use unit (for example, gallons or therms). - Meters and emissions sources
Use the rollup unit set for that commodity category. - Sites and organizations
Use the reporting unit you've selected in Data Reporting Settings (for example, kBtu or MMBtu).
Default system commodities
The following commodities are provided by default.
|
Electric |
| Natural Gas |
| Methane |
| Steam |
| Oil #2 |
| Oil #4 |
| Oil #6 |
| Gasoline |
| Kerosene |
| Propane |
| Coal |
| Energy |
| Water |
| Sewer |
| Hot Water |
| Chilled Water |
| Ice |
| Refuse |
| Recycle |
| Telecom |
| Weather |
| Money |
| Miscellaneous |
| Butane |
| Wood |
| Lighting |
| Ground Transportation |
| Air Travel |
| Diesel Fuel |
| Water and Sewer |
| Irrigation |
| Storm Drainage |
| Internet |
| Cable |
| Fire Protection |
| Solar PV |
| Solar Thermal |
| Wind |
| Biomass |
| Impact Fee |
| Maintenance |
| Influent Plant Flow |
| Ash |
| Biodiesel |
| Chemical |
| Cogeneration |
| Ethanol |
| Liquified Natural Gas |
| Occupancy |
| Oil |
| Mass Transit |
| Reclaimed Irrigation |
|
Reclaimed Water |
| Renewable Electricity |
| Trash |
| Wastewater |
| Well Water |
| Compost |
| Compressed Natural Gas |
| Liquified Petroleum Gases |
| Other Solid Fuels |
| Other Gaseous Fuels |
| Other Liquid Fuels |
| Water Transportation |
| Renewable Natural Gas |
| GHG Emissions |
| Emissions by Cost |
| Emissions by Count |
| Emissions by Weight |
| Carbon Offset |
| Renewable Energy Credit (REC) |